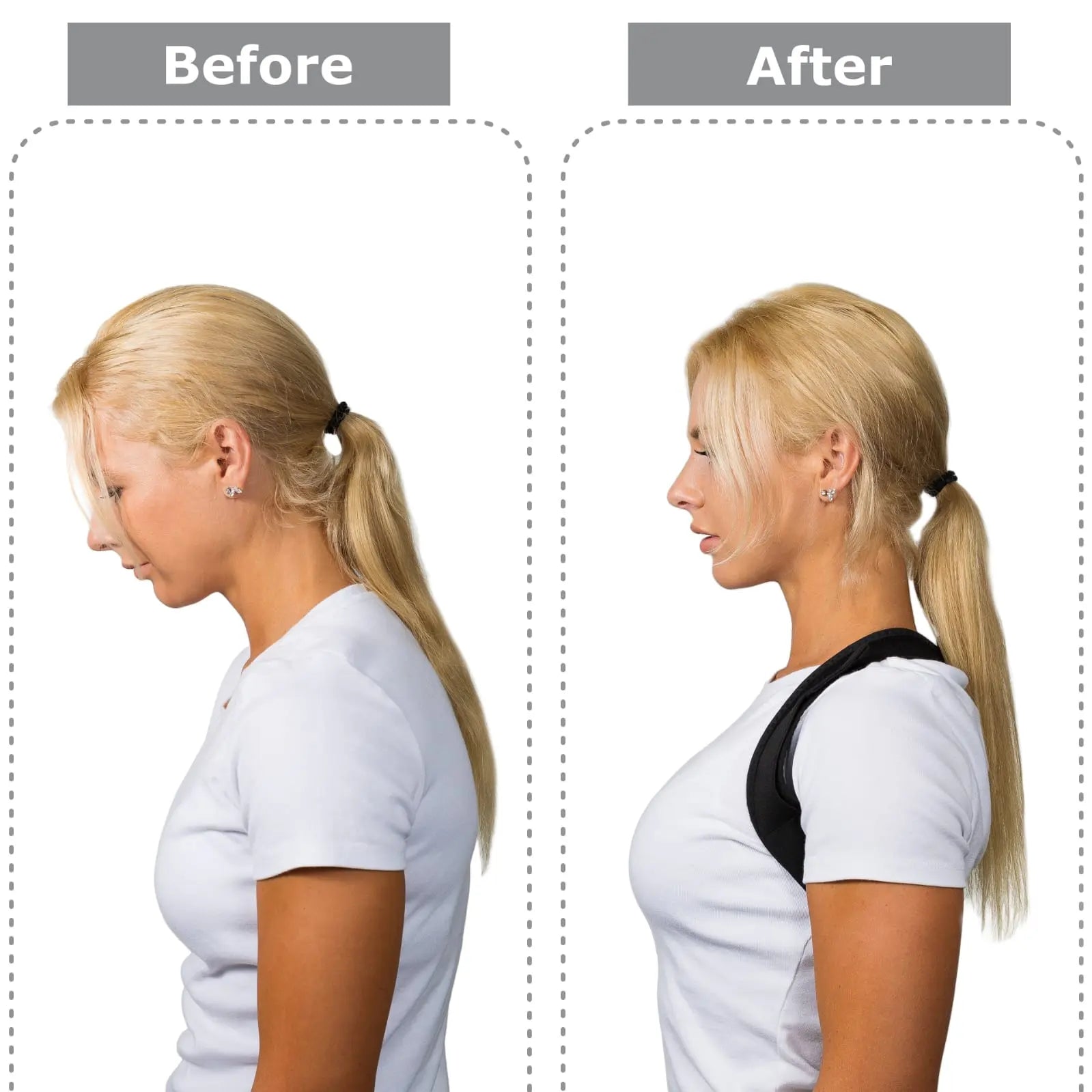
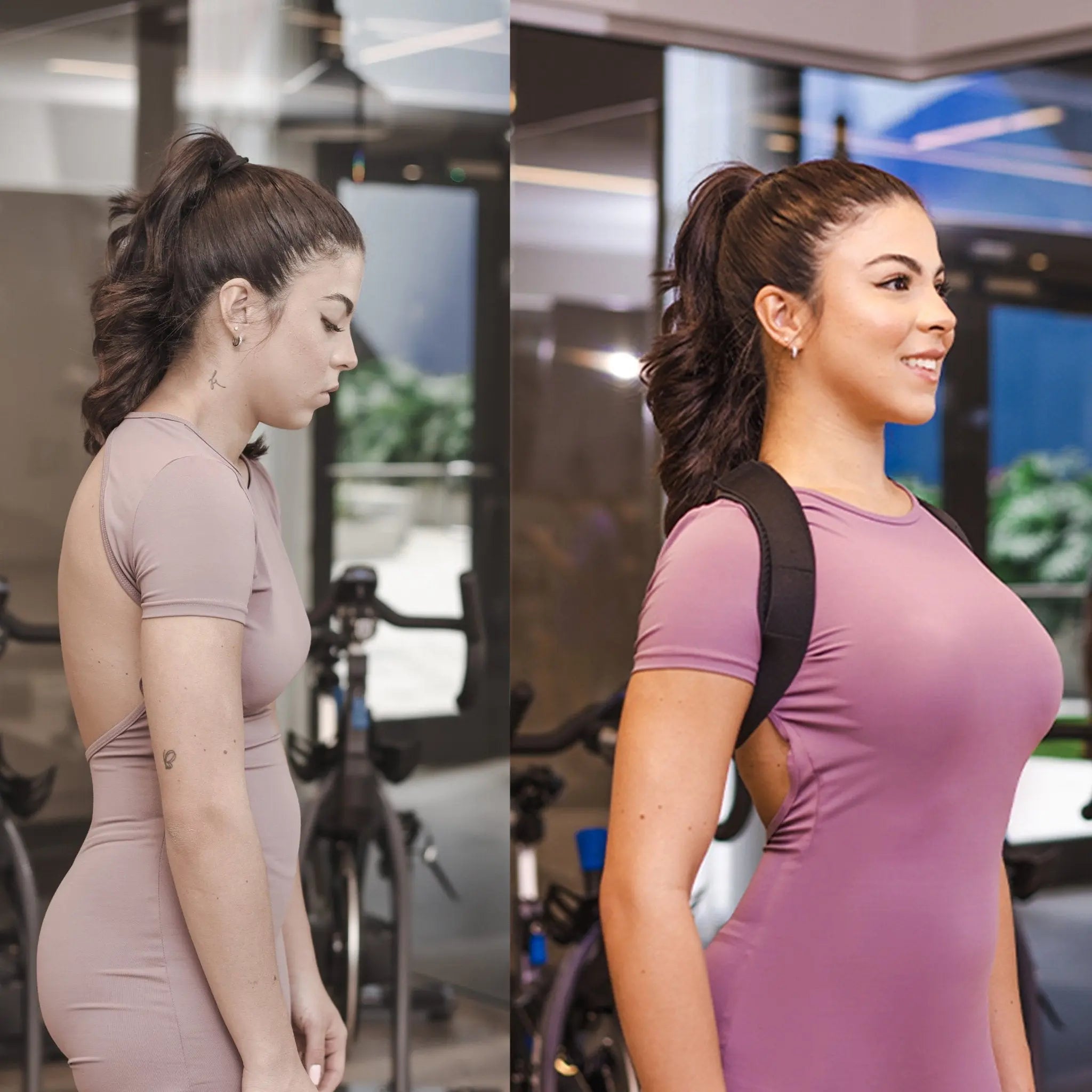
Postural Assessment | How Can It Benefit You?

According to ScienceDirect, Postural Assessment is important to look at a person's posture in different settings. Check if the body is in its best posture regarding muscle, joint, and bone position. It is a necessary medical system.
This can identify health problems that are not normal. Regular difficulty, less movement, and a general loss of health are all possible results of poor posture. Early treatment is essential to prevent any bad situation.
Here, we will discuss postural assessment and what to do and what not to do. As a bonus, you can also find some advice to maintain a healthy posture. So, let’s dive into it.
What is Postural Assessment?
Postural assessment is a way of checking the human body. It is checked when a person is moving or standing. This checking helps improve a person’s posture and identify any abnormalities.
Postural assessments are of two types. One is Static, and another is Dynamic.
- Static Posture: In this posture, the doctor will check the performance of your body when you are standing. This includes different body parts like the shoulder, pelvis, neck, knees, etc.
- Dynamic Posture: It is the opposite of static posture. The doctor will check your body parts when you are moving or walking. Here, mostly muscle performance is the checking part.
Purpose of Postural Assessment
Postural assessment observes your whole body's performance when standing or moving. As per NCBI, postural assessment helps in identifying defects in body.
Different parts of the body are working when you are moving or standing. Doctors can check all the muscles, joints, and alignment through this treatment.
Normally, if you have any abnormalities or imperfections, they can find out and give you the remedy. Sometimes, this assessment can save us from any big diseases.
Benefits of Postural Assessment
The benefits of healthy posture are beyond imagination. So, the usual postural assessment is necessary. This boosts a person physically and mentally. A human body can’t function without a healthy physique and mind.
This benefits energy, concentration, mood, and self-confidence. However, a postural assessment benefits everyone who is health conscious like you. This can be one of the best decisions of your life.
How to Conduct Postural Assessment
You must be curious about how you can conduct this assessment but don’t worry. There are some ways to conduct the postural assessment. Just follow the below steps.
A. Preparing for the Assessment
- Gathering Necessary Tools: Try to gather a measurement tape and a goniometer to measure muscle angle. Assess with proper light and camera setup. Make sure the place is comfortable and safe.
- Creating a Suitable Environment: Try to maintain a safe and sound environment. Keep a chair without hands. Ensure the person is calm and relaxed in the environment.
B. Step-by-Step Assessment Process
1. Observation
- Frontal View
Start with observing the front part of the body. Generally, it is more noticeable when you are standing. Most parts, like the head, neck, shoulder, spine, etc, are part of this frontal view.
- Lateral View
The lateral view is also a significant part of this process. It indicates your side view of the body. Here includes ankle, foot, spinal position, etc.
- Rear View
The rear view completes this observation process. Hip, spine, pelvic foot position, etc, are part of this viewing angle. They all should be in the correct order.
2. Range of Motion Evaluation
There are some steps for a range of motion evaluation. They are described below.
- Start by checking the natural standing position.
- Assess the neck by slowly turning the head from one side to another.
- Move the shoulder from front to sideways.
- Check spine position by bending forward and backward.
- Check the hip mobility by lifting the leg towards your chest.
- Knees need to bend and straight to examine.
- Bending and turning the foot is a good to measure ankle mobility.
- Separate the disabilities and note them.
- Think about the body parts shifting during all these processes.
3. Specialized Tests and Measurements
Doctors may employ different diagnostic tools to get a complete picture of a patient's postural health. Here are three frequent methods:
- Plumb Line Assessment
Doctors usually use plumb line assessments to check their patients' posture. A plumb line is the assessment tool to find out where alignment is off. Remember, maintain a relaxed environment for the person.
- Gait Analysis
This is an important part of the test. Gait analysis means a person’s walking pattern analysis. You need to analyze the walking pattern and identify if there are any abnormalities.
- Functional Movement Screening (FMS)
In this part, you need to analyze the basic part of posturing. Examine the imbalances and disorders. Try to understand what can lead to a bad posture.
Common Postural Deviations
There are different types of common postural deviations. They are:
1. Kyphosis
Due to kyphosis, the upper back can curve around. A person with kyphosis can appear to be slouching. This can affect people of all ages.
2. Lordosis
Extra bend of the lower back and forward head posture defines Lordosis. This is common with osteoporosis patients. Being overweight, wearing heels, or sleeping on the stomach can cause this deviation.
3. Scoliosis
The human body's spine shape is an “S” shape. But for those who have Scoliosis, their back is straight. For this, they have to lean forward to do anything. This can cause back and leg pain as well.
4. Forward Head Posture
You have a forward head posture if your head and neck stick out in front of your shoulders. This happens if you spend a lot of time looking down.
5. Rounded Shoulders
Forward head and shoulder posture are both signs of rounded shoulders. This also causes bad posture.
6. Pelvic Tilt
There are different types of pelvic tilt, like anterior pelvic tilt, posterior pelvic tilt, lateral pelvic tilt, etc. Overall, if your pelvic position doesn’t look normal during assessment, it can be pelvic tilt. The pelvic position defines what type it is.
7. Flat Feet
Flat feet are postural deviations. The feet have a natural curve. You have this deviation if the curve is missing or almost flat to the ground. Sometimes, children are born with this deviation.
8. Knock-Knees and Bowlegs
Knock knees mean when you are standing with straight legs, but your knees are tilted inside. The bowlegs are the opposite. Here, the knees are far away from each other. That can cause discomfort.
9. Other Deviations
Other deviations include winging scapula, duck feet, hiking hips, toe walking, etc. These are all the postural deviations. They have different causes for each deviation. Overall, they all cause bad posture.
Interpreting Postural Assessment Findings
1. Identifying Postural Deviations
Firstly, check the shoulder position. If there are any abnormalities, note them. Then, check the spine and pelvic position. There should be no bending and tilt. After, come to the head section. Look for any extra tilt and forward head posture.
2. Understanding Compensatory Patterns
Find out if your back arch is too extreme because of other weak muscles. Think about the chain reaction this arch could have on the rest of your body.
Now, see if a person starts choosing one foot over the other. This may be a sign of a compensatory process. Check to see if the body seems to stay in balance.
It’s time for knee position. Check if there’s any inward or outward rotation. Think about how this can affect whole body posture.
3. Determining the Root Causes
It’s time for evaluation. The muscles shouldn't be overactive or underactive. This can imbalance the whole-body posture.
Examine if being unable to move some joints is a major issue. Analyze the role that joint limits may have in causing abnormal posture.
Find out how your routine and habits possibly impact your posture. Consider how long you sit, how often you walk, and whether or not your workspace is set up properly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the landmarks for postural assessment?
The landmarks typically used for postural assessment are the earlobe, acromion process, greater trochanter, lateral knee joint line, and lateral malleolus.
How to do postural assessment?
Postural assessment is done by observing your body alignment in static and dynamic positions. This finds out whether you have deviations from the optimal plumb line or not.
Therefore, it also performs tests to assess muscle length, strength, and functional movement.
What are the 5 kinetic checkpoints for the static postural assessment?
The five kinetic checkpoints in the static postural assessment are ankles, knees, hips, shoulders, and ears. They are used as reference points to assess your alignment.
How do you test postural stability?
Postural stability can be tested through various methods. Some of them include single-leg balance tests, the Romberg test, and dynamic balance exercises.
Wrapping Up
Postural assessment is necessary to address any underlying issues that might seem like just the tip of the iceberg initially. Unless you assess your issues, you can never find a proper solution.
So, it’s better to get the assessment done whenever your gut tells you there’s something wrong.